Giant Puffer Fish
 Tetraodon Mbu.
Tetraodon Mbu.A carnivorous freshwater puffer fish that originate from the middle and lower sections of the Congo river in Africa, as well as parts of Lake Tanganyika. It is not sensible, however, to keep these fish with other puffer fish or semi-aggressive fish.
The "puffing" behavior usually occurs when the fish is in danger or stressed, it is therefore not advisable to encourage the fish to 'puff up' on purpose.
It is also dangerous for the fish to 'puff up' with air and so it should only be caught in a volume of water rather than netted. When handling the fish (also not recommended unless absolutely necessary), latex gloves should be worn by the handler since the spines on the fishes skin contain the neurotoxin Tetraodotoxin.
Unlike many other freshwater puffer fish, the Tetraodon Mbu does not benefit from being kept in brackish conditions. It should be kept in a large tank with a clean supply of freshwater with a pH range between 7.0 and 8.0 and a temperature of 24 to 26 degrees C. The water hardness in the tank should be 10 to 12dH.
They are very sensitive to levels of ammonia nitrite and nitrates, so depending on the eating habits and size of aquarium it is highly recommended to regularly conduct 30% water changes every 7 days. One should also remove uneaten pieces of food left in the aquarium.
Remember, whilst the juvenile Mbu may look cute in the aquarium store, they usually grow to 75cm.
It is important to feed a mixture of food to the Mbu not only to ensure they receive plenty of vitamins and minerals, but also eat food sources that contain bones so as to maintain the puffer's beak (teeth). In the wild, Mbu regularly feed on freshwater shellfish such as mussels, and so the beak continues to grow throughout its life to compensate for the abrasive effect of eating shellfish. Thus, if the puffer is fed on a diet of only soft foods, the beak will eventually give the puffer an overbite and prevent it from eating any food.
Photo by Dusko Bojic
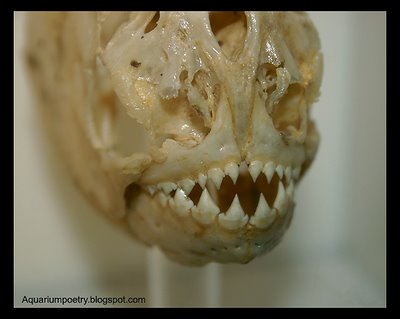
 Piranha originate from Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay and Venezuela.
Piranha originate from Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay and Venezuela. Photos by Dusko Bojic.
Photos by Dusko Bojic.
 Photos by Dusko Bojic.
Photos by Dusko Bojic.

 Photos by Dusko Bojic.
Photos by Dusko Bojic.

